Top
Generation system of seed multiplication
Generation system of seed multiplication is nothing but the production of a particular class of seed from specific class of seed up to certified seed stage. The choice of a proper seed multiplication model is the key to further success of a seed programme which basically depends upon,
a. The rate of genetic deterioration
b. Seed multiplication ratio and
c. Total seed demand
Based on these factors different seed multiplication models may be derived for each crop and the seed multiplication agency should decide how quickly the farmers can be supplied with the seed of newly released varieties, after the nucleus seed stock has been handed over to the concerned agency, so that it may replace the old varieties. In view of the basic factors, the chain of seed multiplication models could be,
a. Three - Generation model
Breeder seed - Foundation seed - Certified seed
b. Four - Generation model
Breeder seed - Foundation seed (I) Foundation seed (II) - Certified seed
c. Five - Generation model
Breeder seed - Foundation seed (I)- Foundation seed (II) -Certified seed (I) - Certified seed (II)
Generation system of seed multiplication
Seed is the cheapest and basic input for sustained agricultural production. At the time of release of a variety, small quantity of seed normally known as nucleus seed is available with the plant breeder. Commercial quantity of seed is produced after a series of multiplication steps. Starting from maintenance programme in which nucleus seed is multiplied in a generation system of multiplication as breeder, foundation and certified seed.
Top
Breeder seed
Breeder seed is produced from nucleus seed under thee supervision of a qualified plant breeder in a research institute of Agricultural University. This provide for initial and recurring increase of foundation seed. Breeder seed is monitored by a joint inspection team of scientists and officials of certification agency and National Seed Corporation. The genetic purity of breeder seed crop should be maintained at 100 per cent.

Breeder seed tag
Tag colour: Yellow
Top
Foundation seed
Foundation seed is the progeny of breeder seed and is produced by State Farm Corporation of India, National Seed Corporation, State seed Corporation under technical control of qualified plant breeders or technical officers. Its production is supervised and approved by certification agency. The genetic purity of foundation seed should be maintained at 99.5 per cent.
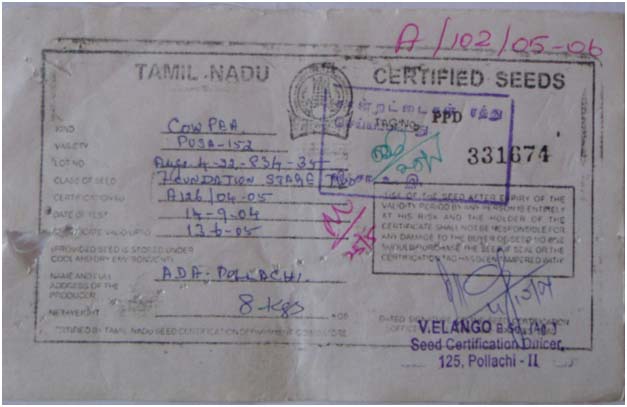
Foundation seed tag
Tag Colour: White
Top
Certified seed
Certified seed is the progeny of foundation seed and its production is supervised and approved by certification agency. The seed of this class is normally produced by the State and National Seeds Corporation and Private Seed companies on the farms of progressive growers. This is the commercial seed which is available to the farmers and its genetic purity should be 99 per cent.

Certified Seed Tag
Tag Colour: Azar blue
Differences between certified seed and truthful labelled seed
| Certified seed |
Truthful labelled seed |
| Certification is voluntary |
Truthful labelling is compulsory for notified kind of varieties |
| Applicable to notified kinds only |
Applicable to both notified and released varieties |
| It should satisfy both minimum field and seed standards |
Tested for physical purity and germination |
| Seed certification officer, seed inspectors can take samples for inspection |
Seed inspectors alone can take samples for checking the seed quality. |
Seed Multiplication Ratio
It is nothing but the number of seeds to be produced from a single seed when it is sown and harvested. According to expert group of seeds (1989), the seed multiplication ratio for different crops are as follows.
| Crop |
Seed Multiplication Ratio |
Crop |
Seed Multiplication Ratio |
| Wheat |
1:20 |
Lucerne |
1:25 |
| Paddy |
1:80 (Varieties) |
Oats |
1:15 |
| |
1:100 (Hybrids) |
Bhendi |
1:100 |
| Maize |
1:80 (Varieties) |
Tomato |
1:400 |
| |
1:100 (Hybrids) |
Brinjal |
1:450 |
| Sorghum |
1:100 |
Chillies |
1:240 |
| Bajra |
1:200 |
Watermelon |
1:100 |
| Ragi |
1:80 |
Pumpkin |
1:160 |
| Gram |
1:10 |
Bittergourd |
1:41 |
| Blackgram |
1:40 |
Bottlegourd |
1:99 |
| Greengram |
1:40 |
Ridgegourd |
1:83 |
| Cowpea |
1:40 |
Cucumber |
1:200 |
| Horsegram |
1:40 |
French bean |
1:9 |
| Moth bean |
1:40 |
Clusterbean |
1:50 |
| Red gram |
1:100 |
Peas |
1:19 |
| Cole crops |
1: 433 |
Onion |
1:171 |
| Potato |
1:4 |
Radish |
1:100 |
| Groundnut |
1:8 |
Carrot |
1:83 |
| Linseed |
1:50 |
Mustard and rape |
1:100 |
| Cotton |
1:50 |
Soybean |
1:16 |
| Jute |
1:100 |
Sunflower |
1:50 |
| Mestha |
1:40 |
Sesame |
1:250 |
| Sunhemp |
1:30 |
Safflower and castor |
1:60 |
| Berseem |
1;10 |
Lucerne |
1:25 |
Top
| 
